Analysis of Material Selection for Aerospace Titanium Alloy Fasteners
Titanium and titanium alloys have a series of advantages such as high specific strength, good corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. They are used more and more in modern aircraft, engines and airborne equipment. The percentage of their use has become an important measure of the advanced nature of aircraft. Sign. The titanium used in the fourth-generation fighter F22A in the United States has accounted for 38. 8 of the structural quality of the aircraft, and some of the Ti 6 Al 4V is used as a fastener. Because the electrode potentials of titanium and carbon fiber composites are similar, titanium alloys become the only joining materials for composite materials. Therefore, with the increasing use of titanium alloys and composite materials for advanced military and civilian aircraft, the demand for titanium alloy fasteners is increasing. At the same strength index, titanium fasteners are 70 times lighter than steel. Moreover, titanium alloys have better fatigue strength and sensitivity to stress concentration than steels of similar use, and high resistance in various climatic conditions. Corrosion stability, so the application of titanium fasteners is very important for aviation equipment. Titanium alloy fasteners have basically replaced alloy steel fasteners on US military and civilian aircraft. The application of foreign titanium alloy fasteners has become very common, and various new types of fasteners have emerged. The use of single-machine titanium alloy fasteners for large civil aircraft reaches hundreds of thousands. For example, a Figure 204 aircraft uses 940kg of BT16 titanium alloy fasteners to reduce the quality of 688kg of a certain advanced military aircraft in the country using titanium alloy fasteners up to 60,000 pieces. Due to the high technical content and complicated process of titanium alloy fasteners, it is mainly concentrated in several specialized chemical plants to produce according to patented technology. Titanium alloy fasteners mainly use three types of materials: the first type is low Mo equivalent type two-phase alloy, such as Ti 6Al 4V, the second type is metastable alloy, and there are American domestic TB2, T B3 and T B8 third. The class is a two-phase alloy of subcritical composition, such as BT in Russia. 16. This work analyzes and compares the different characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of these three types of alloys from the perspective of design selection. 1 fastener material application overview Ti 6Al 4V is a medium strength type two-phase titanium alloy, with excellent comprehensive performance, semi-finished products complete specifications, there are bars, forgings, slabs, sheets, profiles and wire (5mm wire The microstructure of the material is shown in Figure 1). The alloy has a long-term operating temperature of up to 400 and is the most widely used in the aerospace and aerospace industries. It is the primary fastener material used in the aerospace and aerospace sectors in the United States and Western Europe. The United States used one million Ti 6Al 4V titanium alloy bolts in 1955 and reached 20 million in 1958. Fasteners made from this alloy are also used on certain types of aircraft in the country. Russian titanium alloy fasteners mainly use BT 16 titanium alloy. High-strength titanium alloy, analysis of the selection of titanium alloy fasteners for main aviation. The semi-finished products are hot-rolled bars and polished rods for cold heading and wire (see Figure 2 for the microstructure of 5mm wire), which are mainly used for manufacturing fastening. Parts, such as bolts, screws, nuts and rivets, have a maximum working temperature of 350. The strength of the alloy in solution-aging is slightly lower than that of the T i 6A l 4V alloy. The main advantage is that it can be cold-formed under annealed conditions. The lock nut cold turbulent flow line is shown in Figure 3), thus significantly improving production efficiency. Fast-deformed fasteners are widely used in the Russian machinery industry and are the main standard materials used in the Russian aerospace industry. They are also used in certain types of aircraft in the country. The alloy has two states of use: cold deformation strengthening without heat treatment and hot enthalpy forming reinforcement aging treatment. The alloy was included in the AMS4977 specification as a fastener material in 1969 and has some applications on the aircraft, but in 1987 AMS4977B announced that the Aerospace Materials Division recommended that the alloy is no longer used as a standard part material for future new designs. According to recent data, the alloy has stopped production. T i 44. 5N b was included in the AMS4982 specification in 1974 as a special material for rivets, and was revised to AMS4982C in 2002 and is still in use today. But only a small section of the Ti 6Al 4V rivet is welded to the cold riveting. T i 15 3 (TB5) was first introduced as a thin plate in the AM S4914 specification in 1984. T B5 and TB8 are used as matching rivets and screws for the resistance umbrella beam and air hood (high temperature use) in the country. TB2 and T B3 are domestically developed alloys. T B2 was used early on for sheet metal parts and later used as a rivet on some models. TB3 has been used as a material for bolt development and has also been applied to some models. 2 fastener material characteristics fastener performance. The low Mo equivalent type two-phase alloy Ti 6Al 4V has the lowest stability coefficient (only 0.27) and the highest aluminum equivalent (up to 6) in the three types of alloys. Therefore, the phase content in the annealed state is only 7 (volume fraction). It has the advantages of lowest density, best strength and fatigue performance, the simplest composition and the lowest cost of semi-finished products. However, since the plasticity at room temperature is not sufficiently high, the processing of the fastener requires hot pressing for induction heating, and vacuum solution treatment plus aging treatment, and the processing cost is high. 2. The two metastable alloy alloys are completely different, and the stability coefficient is very high, in the range of 1.15 1.97, and the aluminum equivalent is reduced to about 3. Therefore, a single phase can be obtained in the solution treatment, so that the bolts and rivets can be formed by cold rolling at room temperature, and the processing cost is low. The disadvantage is high density, although the strength is comparable to Ti 6Al 4V, but the fatigue performance is not as good as Ti 6Al 4V, and the composition is complicated, and the cost of semi-finished products is high. Since the vacuum aging treatment is also required, the cost of the finished fastener is still higher than that of Ti 6Al 4V, and the use temperature is also lower than that of Ti 6Al 4V. The composition of BT16 alloy is unique. The alloy has the same aluminum equivalent as the second alloy (up to 3). The solid solution strengthening of Al is weakened relative to the Ti 6Al 4V alloy of the first type. However, due to the high content of Mo in the BT16 alloy, the material engineering / 2007 first phase compensated for the lack of Al content, making the alloy highly plastic in the annealed state while maintaining a high strength (aerospace titanium alloy fasteners) Material selection analysis BT 16 alloy stability coefficient is 0.83, between the above two categories, close to the critical component (stability coefficient of 1). In the binary alloy of stable element and Ti composition, with the increase of the content of stable elements, The grain size gradually decreases. Near the critical concentration, the number of phases and phases is equal, and the grain size is minimized. When the stabilizing element is further increased, the grain size increases, as shown in Fig. 4. The smaller grains and the annealed state The phase content of up to 25 (volume fraction) determines the excellent room temperature process plasticity of BT 16 alloy. Therefore, BT16 alloy has the condition of rapid upsetting of the fastener head at room temperature, ie cold heading. Schematic diagram of the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties and phase number of titanium alloy (1) Under annealing condition (2) The relationship between the mechanical properties of BT16 titanium alloy and the degree of cold deformation through reduced diameter in the annealed condition under solid solution aging is shown in Fig. 5. Shown. It is found that when the deformation exceeds about 20, the effect of pre-deformation on the tensile properties of different types of alloys is basically not systematically analyzed with the increase of deformation. The research shows that the alloy consists mainly of phases (BT 1 0 Or the alloy consisting mainly of phases (BT15), the cold deformation strengthening effect is significantly better than the BT16 alloy. ...... It is believed that this phenomenon occurs because the transformation of BT16 alloy under cold deformation and the formation of a metastable phase, while in the alloy mainly composed of phase or phase, such phase does not occur during cold deformation. The transformation, along with the progress of the phase change, the occurrence of dislocation quenching leads to a decrease in the degree of deformation strengthening of the BT16 titanium alloy. This is very important for the manufacture of fasteners with cold heading. The cold head deformation of the fastener head is 75 80 and the neck deformation is 15 20 . Therefore, the annealed BT16 alloy can guarantee the cold heading fastener. Organizational performance uniformity. Relationship with the degree of cold deformation through the reduction method Due to these characteristics of the BT 16 alloy, Russia chose to solve the problem of high processability and high strength characteristics of the fastener manufacturing process (especially when cold rolling). Like the alloy, the BT 16 alloy cold-bolts bolts, rivets and self-locking nuts at room temperature. The rods can also be cold-deformed, necked and rolled, all at room temperature. It is reported in the literature that the workload and cost of manufacturing cold-deformed reinforced fasteners are roughly one-half to one-third that of the first type of Ti 6Al 4V fasteners. The strength and fatigue properties are the same as those of solid solution aging. . The strength and fatigue performance levels are lower than Ti 6Al 4V, TB3. The use temperature of the cold deformation strengthened fastener is specified to be indefinitely used below 160. This temperature range covers most parts of the aircraft. The density of BT 16 alloy is slightly higher than Ti 6Al 4V, but significantly lower than that of alloy. In summary, the first type of Ti 6 Al 4V and the third type of BT16 alloy each have advantages, and the designer can select according to requirements. The second type of alloy has no advantage in manufacturing bolts. It is recommended that the material engineering is no longer recommended. In the case of 2007, the effect of the transfer load of the substrate is gradually reduced, the expansion speed of the crack is delayed, and the bending strength of the composite material is The heat treatment temperature is lowered and the toughness of the material is improved. In addition, as the heat treatment temperature increases, the modulus of carbon fiber and matrix carbon increases, and the modulus of carbon/carbon composite should theoretically increase, but due to heat treatment, the matrix shrinks further, and the interface between carbon fiber and matrix carbon weakens. The modulus of the carbon fiber is not fully exerted, and finally the modulus of the composite material appears to decrease as the heat treatment temperature increases. 3 Conclusions (1) Mesophase pitch-based carbon/carbon composites prepared by pressure impregnation carbonization process, as the heat treatment temperature increases, the graphitization degree of the material increases, the interlayer spacing d decreases, and the crystallite size L increases. . After the material is heat treated by 2500, the degree of graphitization can reach 82. (2) As the heat treatment temperature increases, the flexural strength and flexural modulus of the mesophase pitch-based carbon/carbon composites decrease.å€å€ä¸º1. 30å€ã€‚ The heat-resistant material of the heat-resistant material is 1. 18 times and 1. 30 times. (3) The mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of mesophase pitch-based carbon/carbon composites are related to the interface state of the materials, and the interface bonding is related to the final heat treatment temperature. When the material is not heat treated, the interface is stronger, the bending strength and modulus of the material are higher, the bending fracture is relatively flat, and it has brittle fracture characteristics. As the heat treatment temperature increases, the matrix shrinks further, the interface bond weakens, the flexural strength and modulus of the material decrease, and the bent fracture fibers are pulled out longer, and the material has ductile fracture characteristics. Bolts are used for future new designs, but T B8 alloys can be used under special conditions such as hot oil corrosion, and alloys can be used to make rivets according to design requirements. (1) The work load and cost of cold deformation-reinforced fasteners made of BT16 titanium alloy are the lowest. The alloy fasteners can be used indefinitely below 160. For example, BT16 titanium alloy fasteners in solution-aging state have a long-term working temperature of 350. (2) Ti 6Al 4V fasteners manufactured by enthalpy and vacuum solution treatment have the lowest density, the best strength and fatigue performance, and can be used for a long time below 400. (3) The overall level of bolts made of alloys is lower than that of BT16 and Ti 6Al 4V fasteners, but can be used with cold rivets and where needed. Research and application, contact address: Beijing 81 mailbox 7-box (100095). Materials Engineering / 2007 1
Our company can produce pure Tungsten and Tungsten Alloy milled products, with 99.95% purity for pure tungsten.
We can produce the Tungsten Deep Processing Parts, include Tungsten Screw, tungsten boat, tungsten mesh, tungsten shiled, Tungsten Heating Element and so on.
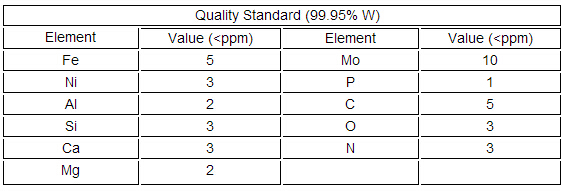
The pure Tungsten Parts chemical compostion
Tungsten Parts Tungsten Parts,Tungsten Heating Element,Tungsten Deep Processing Parts,Tungsten Screw Baoji Shengyuan Metal Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.baojisymetal.com