Application of PDM technology in the implementation of ISO/TS16949:2002 (Figure)
ISO/TS16949:2002 "Quality Management System - Special Requirements for ISO9001:2000 for Automotive Production Parts and Related Maintenance Parts Organizations" is a collection of QS9000, VDA6.1 and other systems. From the perspective of product design, it emphasizes process control and continuous improvement. Defect prevention, in order to reduce the quality fluctuations and waste easily generated in the auto parts supply chain, constitutes a systematic and complete quality management system, reflecting the essence of modern international automotive industry quality management. A large amount of data files and process management of the TS16949 standard requires the help of a computer system. However, in the face of a wide variety of information systems, how to choose the right system to meet the needs of the TS16949 standard implementation process is an urgent problem for automotive supporting companies. The PDM system provides a solution to this problem. Guiding approach. Next page
1. Support for TS16949 by PDM system The PDM system is based on software and takes products as the core. It integrates all product-related information and product development process information into a unified management technology, which can be viewed from two aspects. : Horizontal is the management of products. The PDM system takes the whole life cycle of the product as the main line. It is represented by the representation of the product at different stages of the life cycle. From the sales of BOM to the design of BOM, the process of BOM, the manufacturing of BOM to the production information required by ERP. . The PDM system can help organize product design, improve product structure modification, and timely find archived data and related product information. Vertically, process management, PDM system organizes product development process in the form of project management, and can coordinate organization R&D workflow. Process events such as design review, approval, change, workflow optimization, and product release.
The implementation of the TS16949 standard is closely related to enterprise informationization. The PDM system provides strong technical support and implementation guarantee for the smooth implementation of the enterprise. On the one hand, TS16949 implementation requires strict control of product design features and process characteristics. APQP, PPAP, etc. have developed standard process information; on the other hand, a large number of standardized documents and statistical data are generated during the implementation process. And the statistical process of data must be completed efficiently by means of the large-scale data processing capabilities of computers. Therefore, the implementation of the TS16949 standard is inseparable from enterprise informationization, and the functions of the PDM system are the software support platform for its smooth implementation.
2, PDM system implementation at S16949 standard three focus <br> <br> TS16949 standard implemented in the PDM system, involving project management, configuration management, change management, document management, and almost all of the modules, the need for universal spread in the implementation process Focusing on the fish and grasping its main demand for PDM as a focus, it can be summarized as three aspects: process management, document card editing and document data statistics.
2.1 Process Management (APQP)
APQP is the core tool of 16949, which runs through the entire process of standard implementation. It defines five major phases of enterprise product design, including planning and specification projects, product design and development, process design and development, product and process validation, and feedback, review, and corrective actions.
APQP is a continuous process between stage and stage, logical continuity between process and process, and strong correlation between input and output. Therefore, enterprises should emphasize the application of process method and system method in planning.
PDM project management can manage APQP as a vertical main line to manage the entire product life cycle. For the aforementioned APQP5 large stage, the implementation method in PDM is as follows.
1) Plan and define the project phase. The five large-stage work plans in APQP can be defined and refined in the workflow management, to each work sub-process. When you create a project task, you can reference the workflow as the project and distribute the tasks on it. Each APQP program is unique. Different products have different design procedures. Different customer requirements and expected time and order also affect the complexity of the product. However, the APQP plan for the same product is similar. We can standardize the process of a class of products, establish a generic template, and call it directly during the same product development. Similar product development is used after modification.
The process of project task distribution is to specify the input output of each stage or sub-process on the APQP process template, specify the executor of each stage and sub-process, the task start/end time, and give it the corresponding project role to have it. The corresponding usage rights of the PDM module involved in this project.
2) Product/process design and development phase. After the project is launched, the project members perform their own project roles driven by the workflow and execute the assigned tasks. After submitting the quality documents and drawings submitted by the turtle, the intermediate documents are attached to the project task tree for the project members to view.
3) Product and process validation and feedback phases. The execution process of the task is the execution process of the entire APQP plan. The implementation engineer passes the macro monitoring of the Gantt chart and the implementation of the control plan. The management personnel understand the task status of the project members through the Gantt chart and balance the workload of the personnel.
4) Review and corrective action phases. The archived file changes requirements, and the change management module of PDM can be used to grasp the different change status of the file through version control and new changes. After the change takes effect, the relevant department will be notified in time to accept the feedback confirmation, and the improvement of the implementation and the improvement of the quality will be achieved.
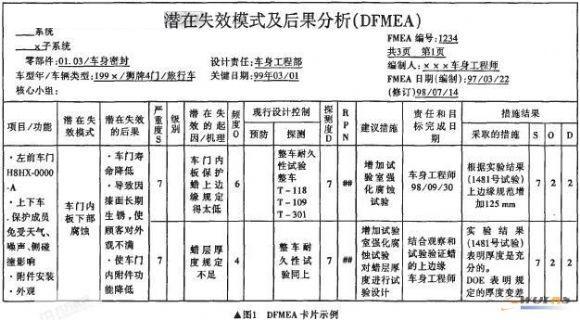
2.2 The writing of document cards (file card template generation and file card association filling) and printing 1) Defining quality file template 2 TS16949 implementation quality file format is relatively standardized, and each type of card can be established by means of CAPP process card drawing function. Templates such as APQP plans, FMEAs, work flow diagrams, and control plans. To define the output, just call the template and fill in the corresponding content. At the same time, it also supports custom document format output, the designer can choose one way according to the situation, as shown in Figure 1.